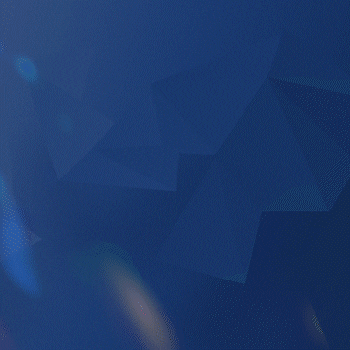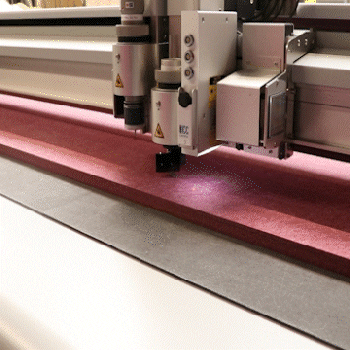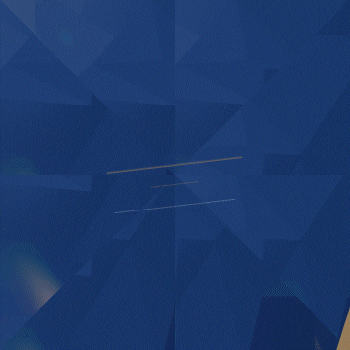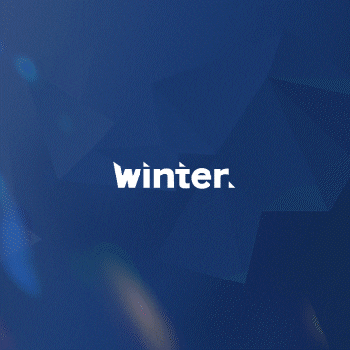
Digital Cutting
Using the digital cutting process, we apply cuts such as V-cuts, grooves, bevel cuts and other cutting and design elements to fleece, textile and leather materials. We mainly cut textile materials, but can also process harder materials such as plastic sheets. Digital cutting is precisely reproducible and enables the production of individual parts at the low cost of series production. Whether pre-printed materials, flexible fabrics, fine cutting contours and details, digital cutting can achieve extreme accuracy.
Digital cutting can be used flexibly: On the one hand, as an upstream production step to prepare the specific shape or size of a workpiece for further processing of the material. However, it is also possible to produce a finished product using cutting alone. If necessary, the cut material can be subsequently glued or finished in a different way to create the desired product.

Advantages of Digital Cutting
Digital cutting is a very quick and easy process. As soon as a cutting pattern is set up, the machine runs autonomously and requires hardly any actions from the employee. Cuts can also be adjusted very easily and quickly. This allows for great flexibility and variety at low programming costs. Variants do not result in longer set-up times in production.
Types of Cuts
V-cuts: As the name suggests, a V-cut is cut into the material from above in a V-shape without cutting through it completely. This results in ridges or grooves of various sizes, which can fulfill aesthetic or functional goals. This cut can be used to make flat material thinner and more flexible and thus realize folds or bends without having to glue several parts together. V-cuts can be cut at different angles depending on what the bending of the workpiece requires.
Bevel cuts: These cuts are angled to create a non-rectangular edge finish, i.e. the edge angle is between 0° and 90°. For this angled cut, the blade is angled along the horizontal, in contrast to miter cuts, for example, where the blade remains vertical and the material is cut at an angle along the vertical. Bevel cuts are well suited for joining corners and for smooth edge transitions.
Cut-outs: Cut-outs are used to cut out part of the material from an inner part. The cut penetrates the entire thickness of the material so that the cut-out remains as a remnant and can be removed. For many products it is necessary to remove a certain shape from the inside of the workpiece, this cut is useful for handles, for example.
Perforations: The material can be cut in such a way that a perforation or hole pattern is created. Perforations can be used to separate material more easily (similar to the edges of a stamp, for example), but they can also fulfill other tasks. Perforations have a clean edge finish and are flexible in size and shape.
Technical Details
Machine Type
Digital Cutting Machine
Size
3200 x 2200 mm
How Digital Cutting Works
Accurate Tuning and Programming
Every project and every material is individual and we also map this process in our company. To do this, we combine CAM-controlled programming with test trials in order to approach the optimal processing.






