Compression Molding
How Molded Nonwovens are Pressed Into Functional 3D Shapes Using Heat and Pressure
The Compression Molding Process for Nonwoven Materials
In the compression molding of nonwovens, the material is first heated in a contact heater to bring it into a malleable state. The nonwoven is then transferred to a special mold and compacted under pressure and cooling until it reaches the desired shape and strength. This process allows nonwovens to be molded into almost any shape without compromising their structural integrity. The result is customized products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Efficient Structure of the Formfleece Process
We produce a wide variety of cases and molded parts with several molding presses. Pressing systems with very large formats and a high pressing force mean that we are equipped to meet the high demands of our customers. We require individual tools for compression molding, but these can be manufactured cost-effectively compared to other production processes. By separating the heating and forming/cooling stations, we achieve short cycle times. In this respect, the cooperation between heating and press module enables us to optimize throughput times. This enables efficient series production for medium-sized batches.
Get to Know the Compression Molding Process in Our Video
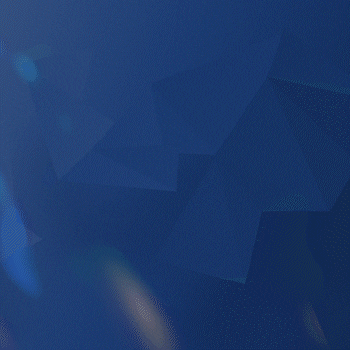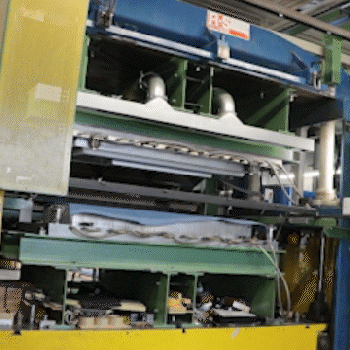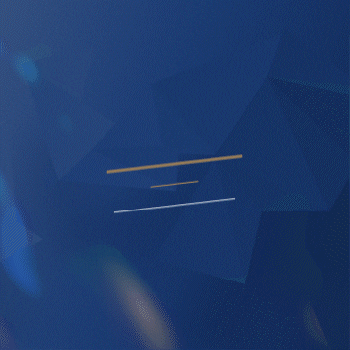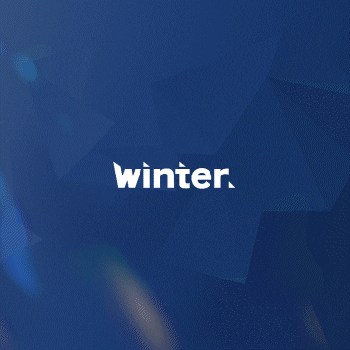
Technical Details of Our Molded Fleece Processing
Machine Types for Pressing Nonwovens
Automated compression molding machines for fleece materials
Work Surface of the Machines
Up to 2000 x 1000 mm (several small formats)
Fleece Materials we Process
We mainly process nonwoven materials in the pressing process. There is a wide variety of materials available here: whether bio-based, degradable or recyclable - we will find the right solution for your project. In our blog post on the different types of nonwoven, we compare their advantages and disadvantages.
Polyester Formfleece: A Recycled Mono-material
Polyester fleece can also be of recycled origin and, as a mono-material, is very easy to recycle. It is ideal for the compression molding of 3D molded parts and is available in many colors and finishes. More about polyester fleece.
Natural Fiber Formfleece: Degradable Hemp Fleece
Natural fiber nonwoven consists of European hemp and a degradable thermoplastic matrix fiber. This means that natural fiber nonwoven is biodegradable and has a strong, natural appearance. More about natural fiber fleece.
Upcycling Textile Formfleece: Used Clothing for 3D Molded Parts
Nowadays, old clothes have hardly any purpose and end up in landfills and incinerators. We want to put them to better use and give them a new life as high-quality 3D molded parts. More about upcycling textile fleece.
Fine Tuning for an Exact Fleece Shaped Part
We are often asked this about 3D compression molding
Molds
Tools are always milled from aluminum. For prototypes we mostly use wood or Ureol.
Quantities
The compression molding process is suitable for medium series. It usually makes sense from about 1,000 parts over its runtime.
Temperatures
Depending on the material, the temperature is approx. 130°-220°. This is also determined by the thickness, properties and desired properties of the final part.
Development time
Generally it takes 4 weeks after the drawings is final to create a prototype. A series tool takes between 8-10 weeks, so that the first series production can usually start after 12 weeks.




